Wildfire
Division of Emergency Management

Wildfire
A wildfire is an uncontrolled fire that spreads through vegetation. Wildfires often start unnoticed and spread quickly, typically first spotted by dense smoke. Hot, dry conditions and high winds can cause fires to grow rapidly. Wildfires can destroy homes, threaten communities, and burn across large areas.
Types of wildfires:
- Wildland fires occur in areas with minimal development, such as remote forests and rangelands
- Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI) fires occur where homes and communities are near forests, grasslands, and brush
What Causes Wildfires
Three elements are needed for fire: heat, oxygen, and fuel. Wildfires can start from lightning strikes, accidents, or intentional acts.
Utah's wildfire risk changes from year to year based on:
- Available vegetation (fuel)
- Snowpack and precipitation levels
- Soil moisture
- Temperature
Once a wildfire starts, vegetation, terrain, and weather determine how fast it spreads.
Wildfire Impacts
Wildfires can:
- Burn thousands of acres
- Destroy homes and property
- Cause injuries and deaths
- Create hazardous smoke and air quality conditions
- Reduce visibility and create dangerous driving conditions from smoke and dust

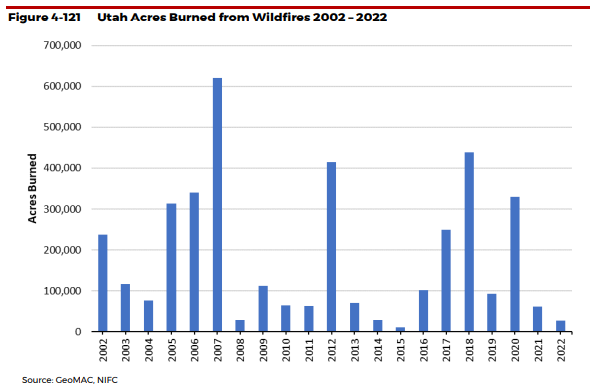
Utah experiences hundreds of wildfires each year, burning tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of acres depending on conditions. Both lightning and human activity cause wildfires.
Recent major wildfires have:
- Burned thousands of acres of forest and rangeland
- Required evacuations of nearby communities
- Created hazardous air quality across the state
- Cost millions of dollars to suppress
Mitigation Case Study: 2012 Seeley Fire

During the summer of 2012, Utah had a particularly active wildland fire season. Fires throughout the state caused considerable damage to resources, infrastructure and personal property. Following this severe fire season, Governor Gary Herbert created the Catastrophic Wildfire Reduction Steering Committee tasked with developing a strategy to reduce the size, intensity, and frequency of catastrophic wildfires in Utah.
Utah lawmakers also authorized approximately $2 million of state funds to create a Catastrophic Wildfire Reduction Strategy that could only be utilized for implementation efforts, primarily fuels mitigation projects. Six regional working groups were established to assess risk and prioritize projects across Utah. As the program matures, the state will improve landscape resilience through fuels mitigation and prescribed fire projects, assist and educate human populations with preparing for and withstanding fire events, and continue to provide and improve timely and effective fire suppression response.













